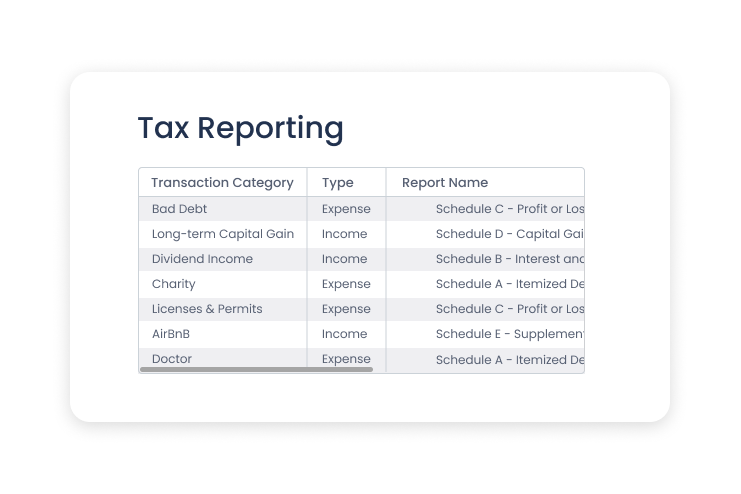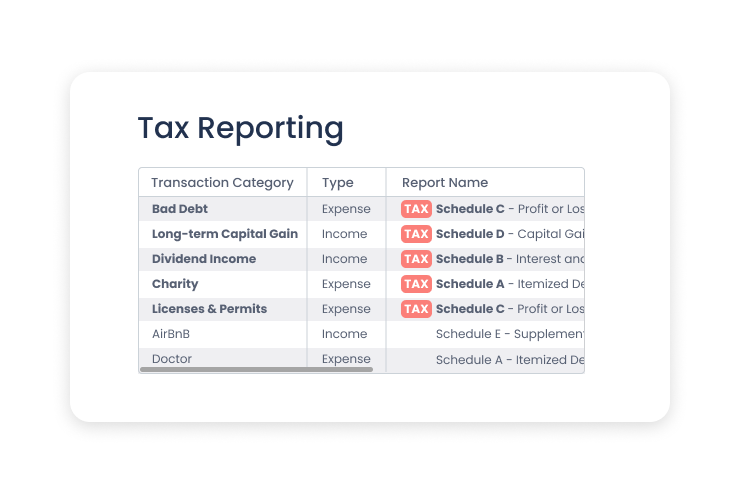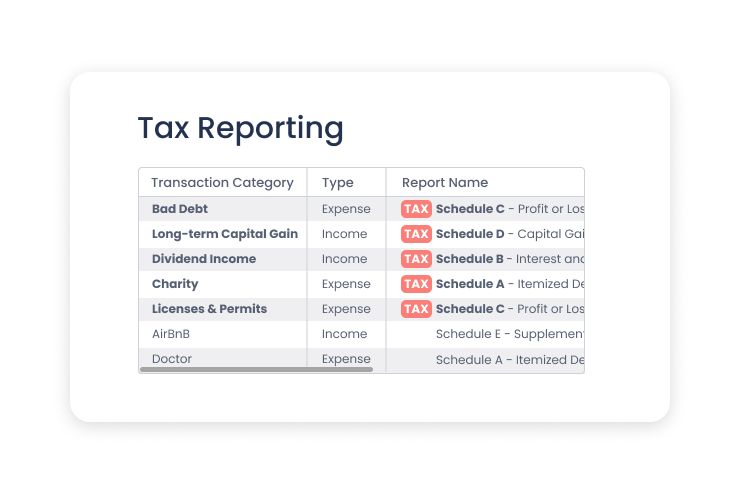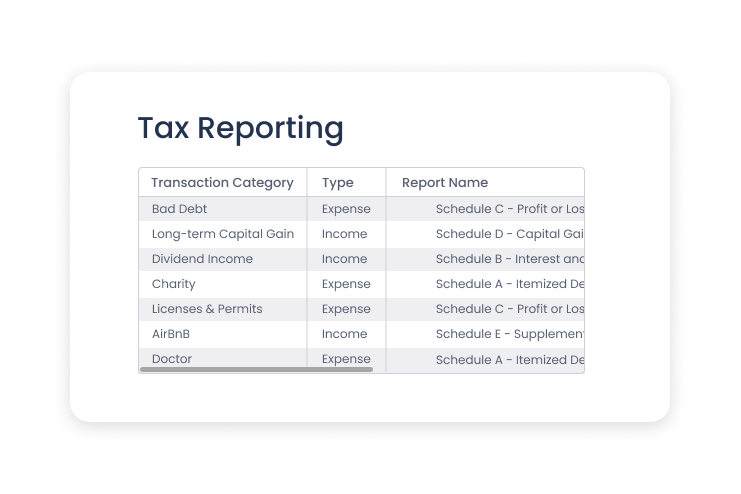
New Tax Reports in Quicken for Mac
Just in time for tax season, Quicken for Mac now offers many new tax reports focused on tax forms and schedules. Want to share them with your accountant or use them in your own tax preparation? Print them out or export them to .csv files, whichever you prefer.
And, of course, the original Tax Schedule report is still available. It combines all the individual tax forms and can be printed or exported to .csv — or even exported directly to TurboTax!
To generate these reports, Quicken uses your transaction categories. For example, an expense categorized as Bad Debt would be tracked on Schedule C under Bad debts from sales/services. If you categorized an expense as Charity, it would be tracked in Schedule A under Cash Charity Contributions.
Here is a list of the schedules Quicken reports on and what they are used for.
Schedule A Tax Form – Report Itemized Deductions
Schedule A is for itemized deductions. It’s used to list certain types of expenses, such as medical and dental expenses, state and local income tax, sales and property taxes, and charitable contributions. These can be used to reduce a taxpayer’s taxable income. Some typical Schedule A categories include Financial Advisor, Charity, Property Tax, Mortgage Interest, and Doctor.
Schedule B Tax Form – Interest & Dividend Income
Schedule B is used to report interest and dividend income on your federal income tax return. This form is typically required if the total amount of your interest and dividend income is over a certain threshold, which is currently $1,500. The form is used to report interest income from banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions, as well as dividend income from stocks, mutual funds, and other investments. Some typical Schedule B categories include Dividend Income and Interest Income.
Schedule C Tax Form – Self-Employed Income
Schedule C is used by individuals who are self-employed to report their income and expenses related to their business. It’s a crucial document for those who run their own business, as it helps them to calculate their net profit or loss, which is then used to determine their income tax liability. It also includes sections for recording depreciation, vehicle expenses, and other deductions that may be relevant to the business.
Overall, the Schedule C Tax Form is an essential tool for self-employed individuals to properly report and pay their taxes. Some typical Schedule C categories include Licenses & Permits (Business), Insurance (Business), and Travel (Business).
Schedule D Tax Form – Capital Gains or Losses
Schedule D is used to report capital gains or losses from the sale or exchange of capital assets. These assets can include stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investments. If an individual has a capital gain, they will owe taxes on the profit made from the sale of the asset. On the other hand, if an individual has a capital loss, they may be able to use it to offset any capital gains they may have had during the year, and potentially lower their overall tax liability.
It’s important to keep accurate records of all capital gains and losses throughout the year, as they will need to be reported on Schedule D. Some typical Schedule D categories include Long-term Capital Gain and Reinvest Long-term Capital Gain.
Schedule E Tax Form – Supplemental Income and Loss
Schedule E is used to report income or loss from rental properties, as well as income or loss from any partnership or S-corporation in which you are a partner or shareholder. This form is particularly important for individuals or businesses who own real estate, as it allows them to report any gain or loss from the sale or disposition of real estate. Quicken does not automatically assign Schedule E to a category, but you can assign this tax line item to a category that already exists, or you can create a new category for it.
Quicken has made the material on this blog available for informational purposes only. Use of this website constitutes agreement to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Quicken does not offer advisory or brokerage services, does not recommend the purchase or sale of any particular securities or other investments, and does not offer tax advice. For any such advice, please consult a professional.
About the Author
John Hewitt
John Hewitt is a Content Strategist for Quicken. He has many years of experience writing about personal finance and payment processing. In his spare time, he writes stories and poetry.